
With a little practice, you’ll be an expert on “choose” versus “chose” in no time. To get familiar with using “choose” versus “chose” in your own writing, try writing a few examples yourself. I chose to skip my date because I wasn’t feeling well.She chose to study physics last semester.We chose to go to Thailand on vacation.When writing about an action in the simple past tense, use the word “chose”: I’m going to choose what to order after seeing the menu.He will choose a college major next year.Use “choose” after an auxiliary verb like “go” or “will” to form the future tense: “Choose” can also be used to describe the future. We need to choose a vacation destination.When writing about an action in the present tense, use the word “choose” or “chooses”, which is the version of “choose” that agrees with a third person subject: “chose” below to help you understand the difference. We provided a few examples of when to use “choose” vs. Sometimes the easiest way to learn a grammar rule is by looking at examples of its application. Luckily, “choosing” and “chosen” are used in very different contexts from “choose” or “chose,” such as, “She is choosing her classes today” and “They have chosen the winning ice cream flavor.” These two additional forms are unlikely to get tangled up in your selection of “choose” versus “chose.” Examples of “choose” vs. There are a couple other forms of “choose” to be aware of when reading and writing “choosing” and “chosen.” “Choosing” is the continuous tense of the verb and “chosen” is the past participle of the verb. For example, the past tense form of the present tense verb “talk” is “talked,” and the past tense form of the present tense verb “watch” is “watched.”īy this logic, it would make sense that the past tense version of “choose” would be “choosed.” However, remember that we mentioned “choose” was an irregular verb? The past tense formation of “choose” as “chose” is one of the ways in which its irregularity appears. Most regular verbs in English become their past tense selves with the application of the ending -ed or -d to the present tense version of the verb. Is the action occurring now? Then select “choose.” Has the action already occurred? Then select “chose.” Why don’t we use the word “choosed”? The key to knowing when to write the word “choose” rather than “chose” is understanding the tense in which you’re writing. “Chose” is the past tense of “choose,” which means that it has the same meaning, but it indicates that the action occurred in the past rather than the present. Indicative presentiAlso known as: present simple or simple present choose chooses simple pastiAlso known as: past simple or preterit chose chose future. The verb “choose” means to pick out or select something from multiple options. “chose”: What’s the difference?Īs mentioned above, “choose” and “chose” are two versions of the same verb-“choose” is present tense” and “chose” is past tense. For irregular verbs, see the Table of irregular verbs in the section called 'Verbs'.Elevate your writing with real-time, intelligent assistance Learn More “Choose” vs.
The past participle of a regular verb is base+ed, e.g.
CHOOSE PAST TENSE PRESENT PLUS
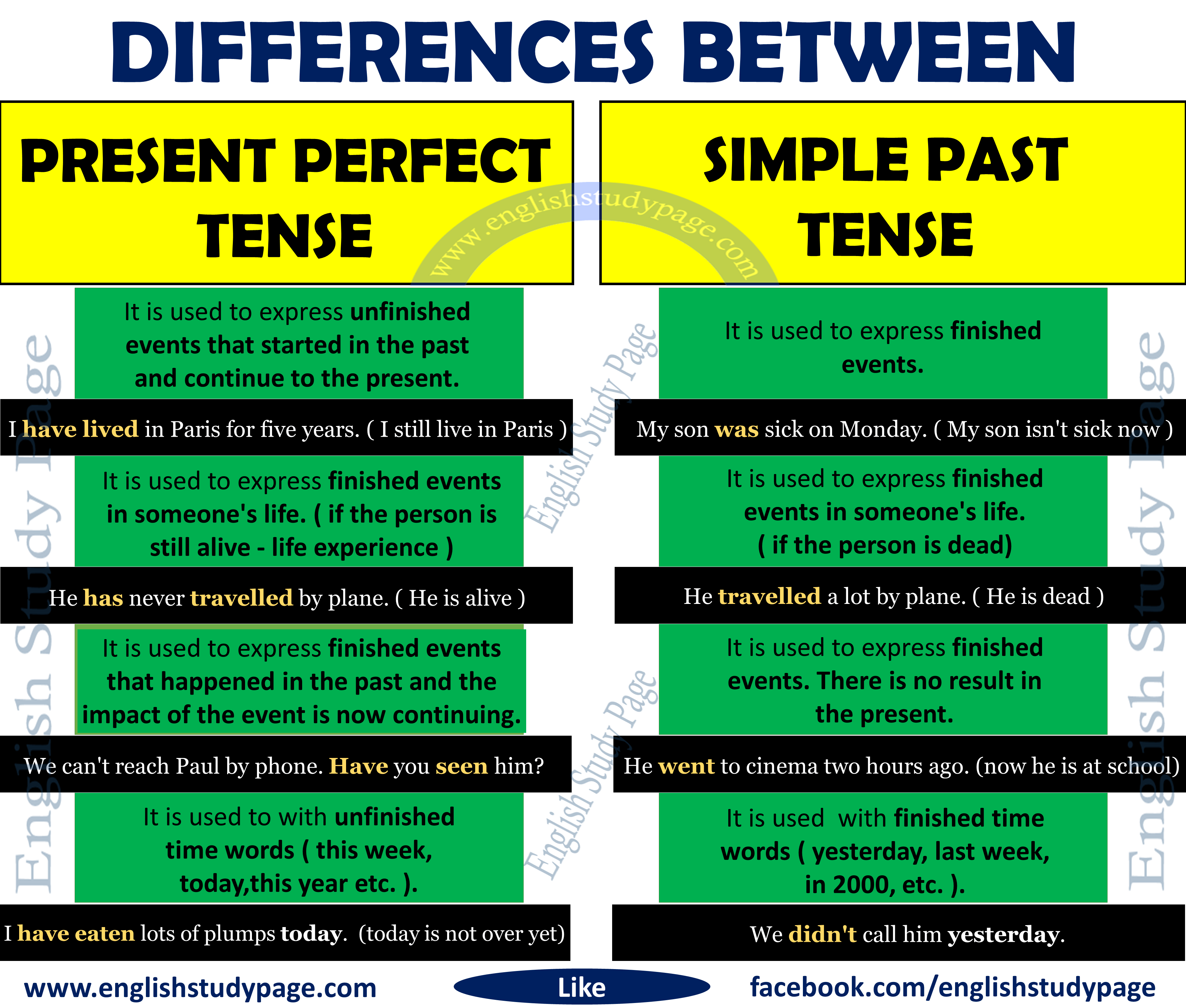
The present perfect of any verb is composed of two elements : the appropriate form of the auxiliary verb to have (present tense), plus the past participle of the main verb. Read more about using the present perfect with the words "ever", "never", "already", and "yet", and about using the present perfect with the words "for" and "since". She's studiedJapanese, Russian, and English.When the precise time of the action is not important or not known



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
